– credit Fujikawa et al. with background / SWNS
If a physician needs to see what’s gone wrong inside a human body, it’s easy enough to order an ultrasound scan. But if the structural engineer wants to do the same in a block of concrete, his options are of limited effectiveness.
The range of materials that concrete contains, such as stone, clay, chalk, slate, iron ore, and sand, scatters normal sound waves, making clear images difficult to obtain.
Now, Japanese and American scientists have teamed up to develop a system that can identify interior defects in concrete buildings and bridges without destroying their structure.
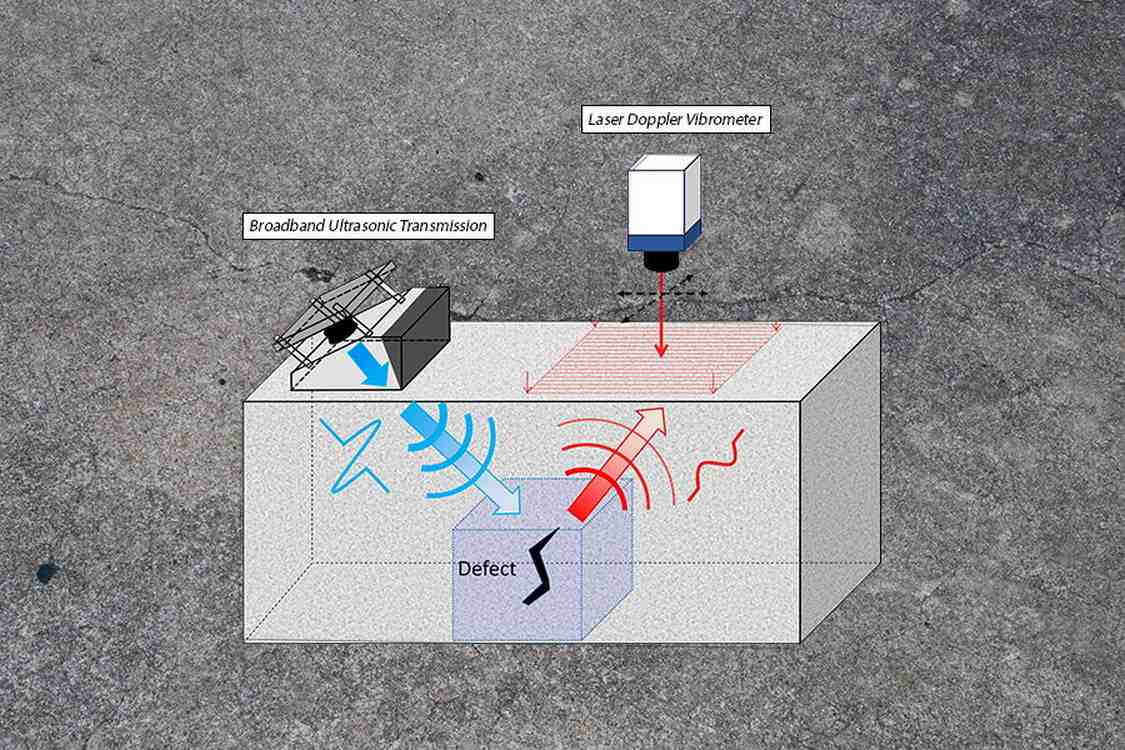
Team members explain in a news release that their method sends sound waves into the material and captures the waves that echo back to create images of what’s inside, just like an ultrasound.
“In our approach, the ultrasonic wave is broadband, using a wide range of ultrasonic frequencies rather than operating around a single, fixed frequency,” said Professor Yoshikazu Ohara from Tohoku University in Japan.
“The receiver is capable of accepting an even broader range of frequencies. By automatically adapting the frequency to the material, our system improves the contrast between defects and background material in concrete.”
Tohoku and his colleagues joined the Los Alamos National Laboratory in New Mexico, and Texas A&M University to create the system.
A chief challenge is that it’s hard to know which frequencies of sound waves will survive traveling through concrete, as different material therein may interfere with different wavelengths.
To accommodate the uncertainty, the team used two devices: one to generate a wide range of frequencies to send into the material and another, called a vibrometer, to capture the outcoming waves.
The system, described in the journal Applied Physics Letters, can handle a wide range of frequencies, which means that even if ultrasonic waves are scattered by materials in the concrete, those that do make it through are still detected, regardless of what frequency they are.
“As the concrete filters out certain frequencies, the laser Doppler vibrometer simply captures whatever frequencies remain,” said Professor Ohara. “Unlike conventional systems, we don’t have to swap transducers or adjust the frequency beforehand. The system adapts automatically.”
The result is a high-resolution 3D image of the defect and its location in the concrete.For a repair planner or field technician, this provides ‘concrete’ information: how deep the defect is from the surface, how large it is, and how it extends in three dimensions, making it possible to plan repairs more efficiently. New Ultrasonic Imaging System Can Detect Deadly Defects in All Types of Concrete


_11126.jpg) The uranium battery concept (Image: JAEA)
The uranium battery concept (Image: JAEA)
 credit – Adrian Sulyok on Unsplash
credit – Adrian Sulyok on Unsplash.jpg?ext=.jpg)

