Antarctica gaining more ice than it's losing: NASA
Antarctica has a huge, completely hidden mountain range. New data reveals its birth over 500 million years ago
Have you ever imagined what Antarctica looks like beneath its thick blanket of ice? Hidden below are rugged mountains, valleys, hills and plains.
Some peaks, like the towering Transantarctic Mountains, rise above the ice. But others, like the mysterious and ancient Gamburtsev Subglacial Mountains in the middle of East Antarctica, are completely buried.
The Gamburtsev Mountains are similar in scale and shape to the European Alps. But we can’t see them because the high alpine peaks and deep glacial valleys are entombed beneath kilometres of ice.
How did they come to be? Typically, a mountain range will rise in places where two tectonic plates clash with each other. But East Antarctica has been tectonically stable for millions of years.
Our new study, published in Earth and Planetary Science Letters, reveals how this hidden mountain chain emerged more than 500 million years ago when the supercontinent Gondwana formed from colliding tectonic plates.
Our findings offer fresh insight into how mountains and continents evolve over geological time. They also help explain why Antarctica’s interior has remained remarkably stable for hundreds of millions of years.
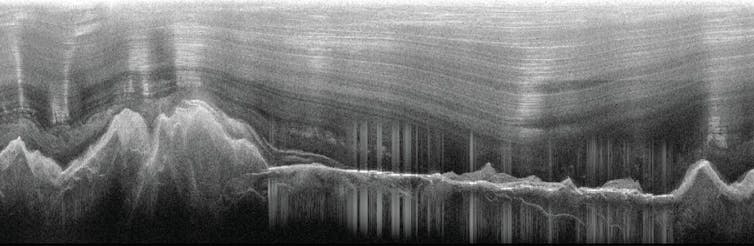 A radar image showing the Gamburtsev mountain range under layers of ice. Creyts et al., Geophysical Research Letters (2014), CC BY-SA
A radar image showing the Gamburtsev mountain range under layers of ice. Creyts et al., Geophysical Research Letters (2014), CC BY-SAA buried secret
The Gamburtsev Mountains are buried beneath the highest point of the East Antarctica ice sheet. They were first discovered by a Soviet expedition using seismic techniques in 1958.
Because the mountain range is completely covered in ice, it’s one of the least understood tectonic features on Earth. For scientists, it’s deeply puzzling. How could such a massive mountain range form and still be preserved in the heart of an ancient, stable continent?
Most major mountain chains mark the sites of tectonic collisions. For example, the Himalayas are still rising today as the Indian and Eurasian plates continue to converge, a process that began about 50 million years ago.
Plate tectonic models suggest the crust now forming East Antarctica came from at least two large continents more than 700 million years ago. These continents used to be separated by a vast ocean basin.
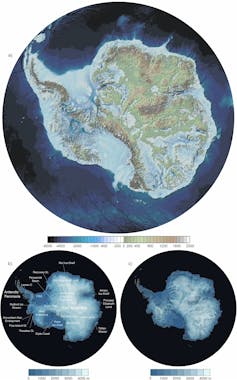 A map of the topography (a) and surface elevation (b) of Antarctica, measured in metres above sea level; (c) shows ice thickness in metres. Pritchard et al., Scientific Data (2025), CC BY
A map of the topography (a) and surface elevation (b) of Antarctica, measured in metres above sea level; (c) shows ice thickness in metres. Pritchard et al., Scientific Data (2025), CC BYThe collision of these landmasses was key to the birth of Gondwana, a supercontinent that included what is now Africa, South America, Australia, India and Antarctica.
Our new study supports the idea that the Gamburtsev Mountains first formed during this ancient collision. The colossal clash of continents triggered the flow of hot, partly molten rock deep beneath the mountains.
As the crust thickened and heated during mountain building, it eventually became unstable and began to collapse under its own weight.
Deep beneath the surface, hot rocks began to flow sideways, like toothpaste squeezed from a tube, in a process known as gravitational spreading. This caused the mountains to partially collapse, while still preserving a thick crustal “root”, which extends into Earth’s mantle beneath.
Crystal time capsules
To piece together the timing of this dramatic rise and fall, we analysed tiny zircon grains found in sandstones deposited by rivers flowing from the ancient mountains more than 250 million years ago. These sandstones were recovered from the Prince Charles Mountains, which poke out of the ice hundreds of kilometres away.
Zircons are often called “time capsules” because they contain minuscule amounts of uranium in their crystal structure, which decays at a known rate and allows scientists to determine their age with great precision.
These zircon grains preserve a record of the mountain-building timeline: the Gamburtsev Mountains began to rise around 650 million years ago, reached Himalayan heights by 580 million years ago, and experienced deep crustal melting and flow that ended around 500 million years ago.
Most mountain ranges formed by continental collisions are eventually worn down by erosion or reshaped by later tectonic events. Because they’ve been preserved by a deep layer of ice, the Gamburtsev Subglacial Mountains are one of the best-preserved ancient mountain belts on Earth.
While it’s currently very challenging and expensive to drill through the thick ice to sample the mountains directly, our model offers new predictions to guide future exploration.
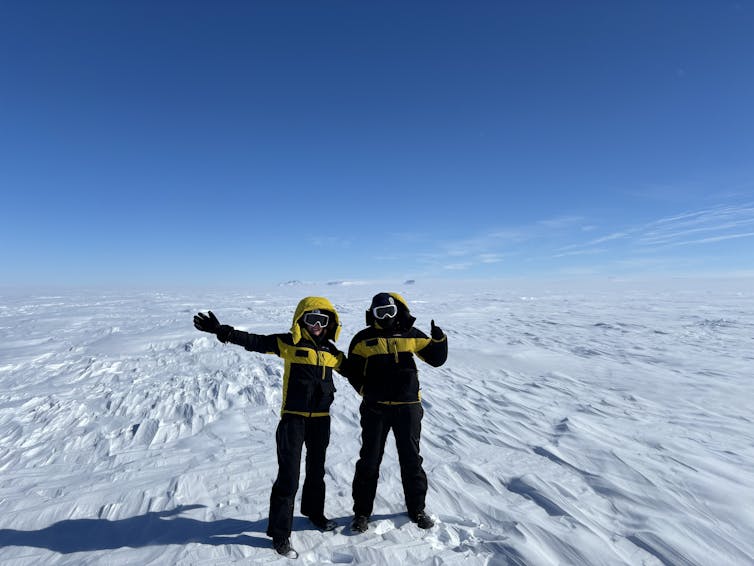 Geologists Jacqueline Halpin and Jack Mulder stand on the Denman Glacier during recent fieldwork. Jacqueline Halpin
Geologists Jacqueline Halpin and Jack Mulder stand on the Denman Glacier during recent fieldwork. Jacqueline HalpinFor instance, recent fieldwork near the Denman Glacier on East Antarctica’s coast uncovered rocks that may be related to these ancient mountains. Further analysis of these rock samples will help reconstruct the hidden architecture of East Antarctica.
Antarctica remains a continent full of geological surprises, and the secrets buried beneath its ice are only beginning to be revealed.![]()
Jacqueline Halpin, Associate Professor of Geology, University of Tasmania and Nathan R. Daczko, Professor of Earth Science, Macquarie University
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.

