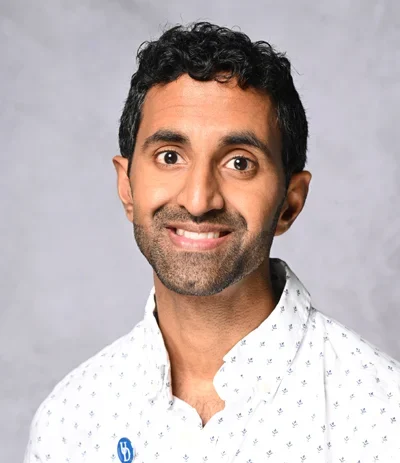
Aditja Kunjapur PHOTO: AAAS.org
Biomolecular engineer Aditya Kunjapur, assistant professor at the University of Delaware, Newark, Delaware, recently won the 2024 BioInnovation Institute & Science Prize for Innovation,
Kunjapur and his colleagues have found a way to create bacteria that build and incorporate a key amino acid into their own proteins, making it easier to fight infections.
For this work toward building a better platform for possible ifuture bacterial vaccines, Kunjapur is the winner of the 2024 BioInnovation Institute & SciencePrize for Innovation, the American Association for the Advancement of Science announced April 5, in a news item on aaas.org.
“The prize seeks to reward scientists who deliver research at the intersection of the life sciences and entrepreneurship,” it noted.
“Dr. Kunjapur’s outstanding research demonstrates the potential to engineer live bacterial cells to produce and incorporate nitrated amino acids into antigenic proteins, thus shining a spotlight on these proteins for the human immune system,” Michael Funk, senior editor at Science is quoted saying in the new release. “This work provides a platform for antigen engineering that is adaptable, specific, and amenable to safety controls.”
Vaccines against bacterial infections would likely decrease the need for antibiotic medicines, which in turn could stem the development of antibiotic resistance in some key drugs, AAAS noted.
Kunjapur estimates that bacterial vaccines will have an estimated global market size of $39.6 billion by 2030.
In his winning essay published April 5 in Science, Kunjapur writes — “our primary hypothesis is that engineering cells to access a broader chemical repertoire of building blocks can improve live bacterial vaccine efficacy.”
According to the news report, Kunjapur saw potential in a building block from earlier research in which a bacterial protein was modified with a non-standard amino acid called para-nitro-L-phenylalanine (nitro-Phe). The combination “triggered sustained production of antibodies in mice, suggesting that the altered amino acid was making it easier for the immune system to access or recognize the bacterial protein,” the news report noted.
Kunjapur and colleagues programmed E. coli bacterial cells to produce their own nitro-Phe and incorporate it into target proteins. The altered proteins hold the potential of becoming the basis for a live bacterial vaccine, the researchers suggest.
“In principle, the nitro-Phe modified protein produced by the engineered bacteria within a patient would lead to a targeted, sustained, and protective immune response towards bacterial pathogens,” even versions of the protein that haven’t been nitrated, Kunjapur is quoted saying.
Kunjapur also indicated that his team’s bioengineering strategy could work with other bacteria as well, not just E coli.
“We could also continue to use E. coli as a platform vector that makes recombinant proteins that belong to other bacteria,” he said. “So you can pick your chassis or your protein delivery vehicle, but the proteins you choose to nitrate should determine what immune cells respond to.”
Kunjapur hopes to work toward a vaccine for staph infections. The Covid pandemic came in the way of procuring funding for expanding his work, so Kunjapur used his own funds for the patent application.
“At the time I had cautious optimism in investing in new potential vaccine modalities during the height of a pandemic, but a lot of it was also a bet on the people behind the idea and our collaborators,” he said.
Kunjapur co-founded Nitro Biosciences, Inc. with his postdoc, Neil Butler, to pursue the nitro-Phe technology. He said starting the company has made him think more about who is going to use the technology, and what kind of criteria and metrics they need to know so that it can be used successfully.
The BioInnovation Institute & Science Prize for Innovation, the editors of Science “seek to recognize bold researchers who are asking fundamental questions at the intersection of the life sciences and entrepreneurship. We seek scientists who can show that they have reached across field boundaries with an enthusiasm that combines outstanding basic science with an eye toward application in the marketplace,” Science.org says on its website.
Located in Copenhagen, Denmark, the BioInnovation Institute foundation (BII) is an international commercial foundation with a nonprofit objective supported by the Novo Nordisk Foundation. “BII operates an incubator to accelerate world-class life science innovation that drives the development of new solutions by early life science start-ups for the benefit of people and society,” the Science.org website said. University of Delaware professor wins top bio-innovation prize