 BirdCast
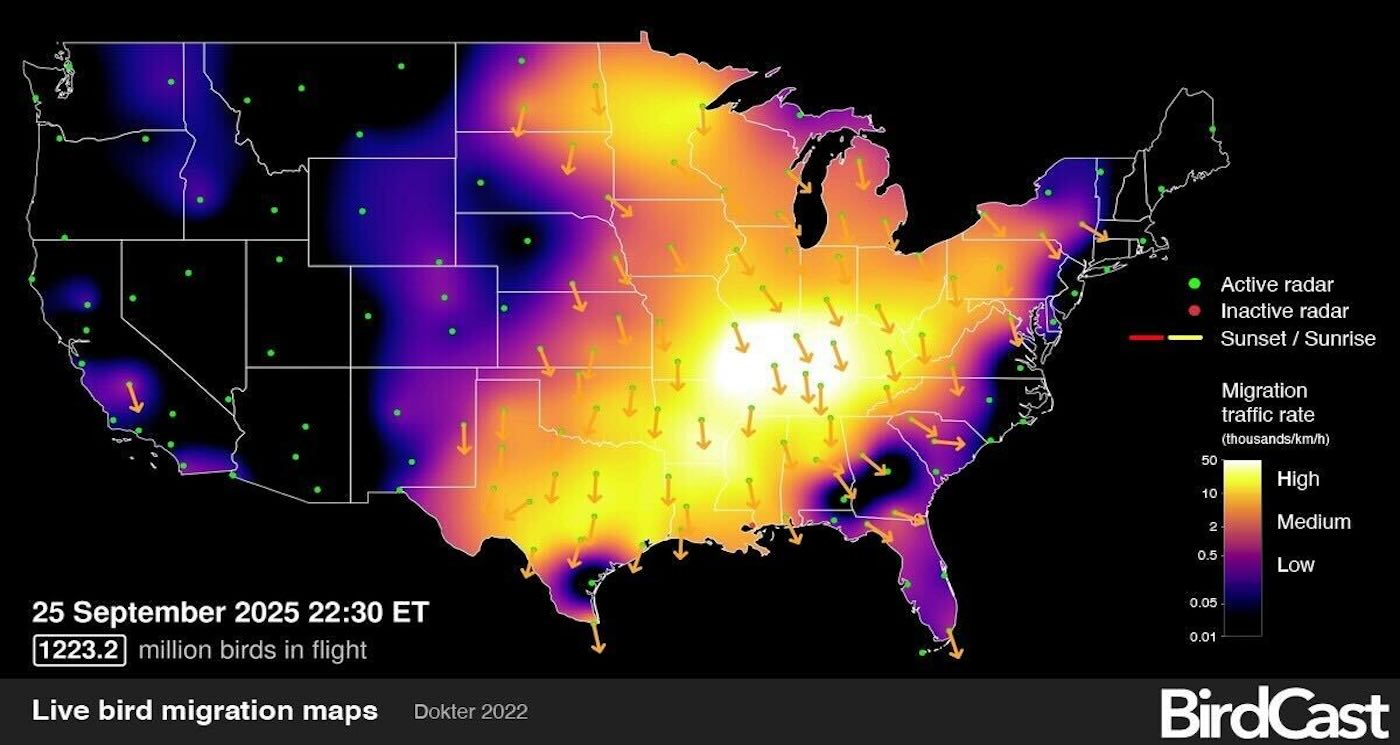
BirdCastMore than 1.2 billion birds streamed south in one night during their Fall migration in late September—the largest single-night total ever recorded by the American live radar project.
Called BirdCast, a collaboration led by the Cornell Lab of Ornithology, the platform uses the same weather radar technology behind daily forecasts to track migrating birds.
On its live migration map, BirdCast tracked more than 1.2 billion birds streaming toward their wintering grounds after sunset on September 25—the largest single-night total recorded since the project began mapping live migrations in 2018.
“These numbers are almost inconceivable,” said Andrew Farnsworth, a visiting scientist at the Cornell Lab of Ornithology and longtime BirdCast researcher. “They’re enormous… even for people that study migration regularly. The scale of how many organisms that this represents, is just mind blowing.”
The surge surpasses the previous milestone of one billion birds, first observed during the migration in October 2023. Both included well over one hundred species flying toward warmer weather, including songbirds and shorebirds.
Farnsworth said this seemingly rare night captured about 10% of the continent’s birds in flight at the same time. On an average fall night during peak migration, about 400 million birds are detected in flight at the same time above the United States, but on this night, the number was three times that.
“It’s really unbelievable,” he said.
While astonishing to both birders and scientists, Farnsworth said this event was not random. It resulted from a combination of ideal migrating conditions coinciding with the peak of fall migration.
The weather that night was perfect for travel, he explained in a media release. It featured calm winds—including tail winds that helped push the birds along their migratory paths across much of the center of the country and the Mississippi River valley.
Farnsworth said this record-breaking migration—documented by radar technology that was never intended to track birds—is a chance to not only to marvel at the immense magnitude of bird migration but also a chance to remind the public that the data is freely available and accessible in real time.
The technology at BirdCast.org allows anyone to view forecast maps that predict the number of birds migrating while live migration maps show migration happening in real time. Both tools let people know when birds are moving nearby, so they can take necessary precautions to protect them.
“BirdCast gives the ability for more people to engage in and participate in this incredible spectacle,” Farnsworth said, whose Cornell Lab partners with three US universities in the project: Purdue, Illinois Urbana-Champaign, and Massachusetts Amherst.
It’s also a timely reminder that you can help make birds’ journeys safer. Every year, more than one billion birds die in collisions with windows in the United States.
Bright lights can disorient birds migrating at night, drawing them into areas where collisions with glass are common. To assist our feathered friends, turn off nonessential lights at night. You can also add bird friendly film or other markings on the outside of windows. Learn more at stopbirdcollisions.org. Record-Breaking Night of Bird Migration Caught on Radar During a ‘Perfect Storm’ for Feathered Flight

