Cnemaspis vangoghi – Akshay Khandekar
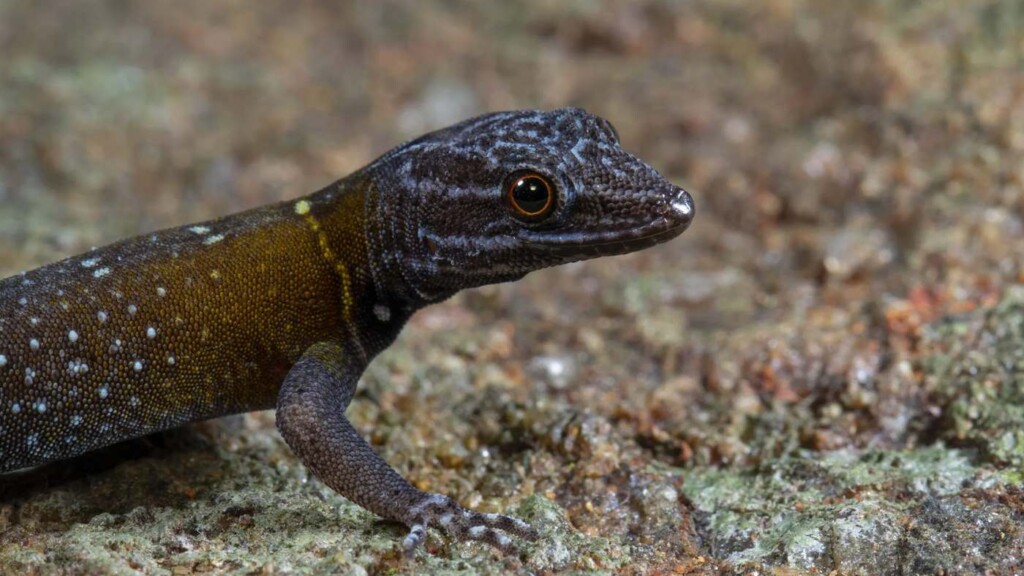
Cnemaspis vangoghi – Akshay KhandekarIn India’s remote Western Ghats, a gorgeous blue and yellow gecko species has been named in honor of Vincent Van Gogh, whose painting Starry Night, was the first thing that entered Ishan Agarwal’s mind when he saw it.
Found during one of many expeditions into these underdeveloped, underexplored mountains running parallel to India’s western coastline, it enriches both the eyes and the scientific literature.
Belonging to the genus Cnemapsis, it is one of 2,300 members worldwide and over one hundred in India alone. Not so long ago, however, there were only a few dozen.
“We have incredibly diverse fauna, but we know little about it,” Agarwal told Nat Geo of the Western Ghats, in which he has spent 12,400 hours exploring.
Cnemapsis vangoghi was found during one such exploration, after the flash of indigo and mustard yellow which caught Agarawl’s eye.
It looked similar to another gecko of the same genus, C. galaxia, but during lab work, his suspicions were confirmed that it was actually a new species. It and a second, closely related species, are described for the first time in a study published in the natural ZooKeys.
Found in the Srivilliputhur-Megamalai Tiger Reserve, Agarawl suspects that this gecko is receiving much greater protection than many of India’s native reptiles because of its location under the ‘umbrella’ of the charismatic cat.
Umbrella conservation strategies allow naturalists to advocate for the conservation of a single species whose needs of territory, prey species, and protection are largest, and ipso facto helps conserve dozens or even hundreds of other species that share that territory.
In this case, protecting tigers means protecting geckos.
Agarwal says that new techniques for studying DNA allow for much greater specificity in describing species, and that the genus Cnemapsis is “ridiculously diverse.”Biologist Finds Beautiful Blue Gecko, Named the New Species 'Vangoghgi'