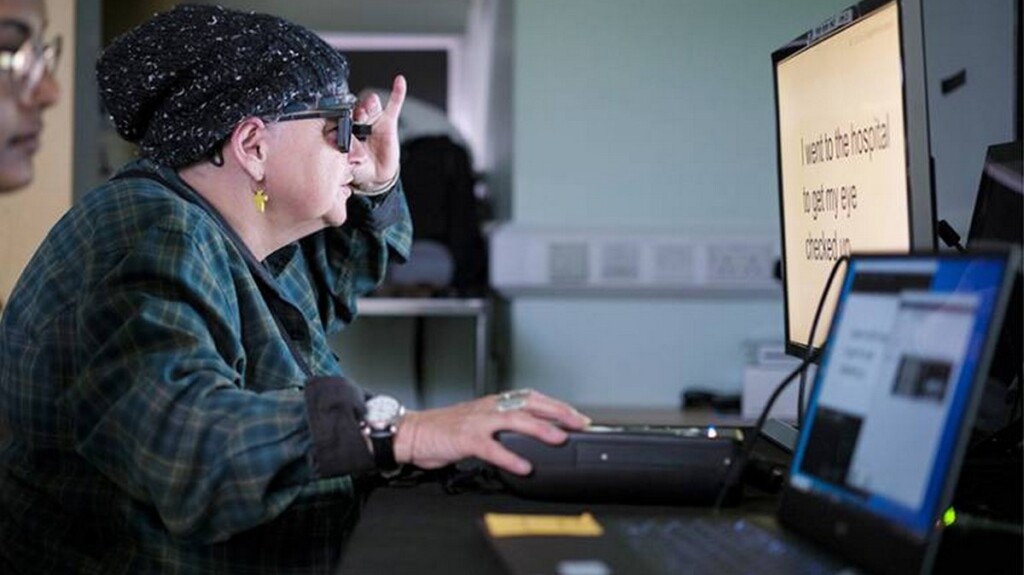
Study participant Sheila Irvine training with the device – credit Moorfields Eye Hospital
Study participant Sheila Irvine training with the device – credit Moorfields Eye HospitalA “new era” has begun in the development of artificial vision after a combination electronic eye implant—with augmented reality glasses restored vision to blind eyes in patients with untreatable macular degeneration.
Those treated with the device could read, on average, five lines of a vision chart, even though some could not even see the chart before their surgery.
The results of the European clinical trial which involved 38 patients in 17 hospitals across 5 countries were published in The New England Journal of Medicine. They showed 84% of participants were able to read letters, numbers, and words using prosthetic vision through an eye that had previously lost its sight due to the untreatable progressive eye condition, “geographic atrophy with dry age-related macular degeneration (GA in dry AMD).”
The now-proven device is called PRIMA, and consists of an ultra-thin microchip implanted in the eye that receives infrared projections of the waking world by a video camera installed in a pair of augmented reality classes.
A pocket computer fixed to a small control panel worn on the waistband then runs artificial intelligence algorithms to process the information contained in the infrared projection, which is converted into an electrical signal. This signal passes through the retinal and optical nerve cells into the brain, where it’s interpreted as vision.
The patient uses their glasses to focus and scan across the main object in the projected image from the video camera, using the zoom feature to enlarge the text. Each patient goes through an intensive rehabilitation program over several months to learn to interpret these signals and start reading again.
“In the history of artificial vision, this represents a new era,” said Mr. Mahi Muqit, associate professor at the UK’s University College London’s Institute of Ophthalmology and consultant at Moorfields Eye Hospital where the UK arm of the trial was conducted.
“Blind patients are actually able to have meaningful central vision restoration, which has never been done before.”
“Getting back the ability to read is a major improvement in their quality of life, lifts their mood and helps to restore their confidence and independence. The PRIMA chip operation can safely be performed by any trained vitreoretinal surgeon in under two hours—that is key for allowing all blind patients to have access to this new medical therapy for GA in dry AMD.”
Dry AMD is a slow deterioration of the cells of the macula over many years, as the light-sensitive retinal cells die off. For most people with dry AMD, they can experience a slight loss of central vision.
Through a process known as geographic atrophy (GA), it can progress to full vision loss in the eye, as the cells die and the central macula melts away. There is currently no treatment for GA, which affects 5 million people globally. All participants in this trial had lost the central sight of the eye being tested, leaving only limited peripheral vision.
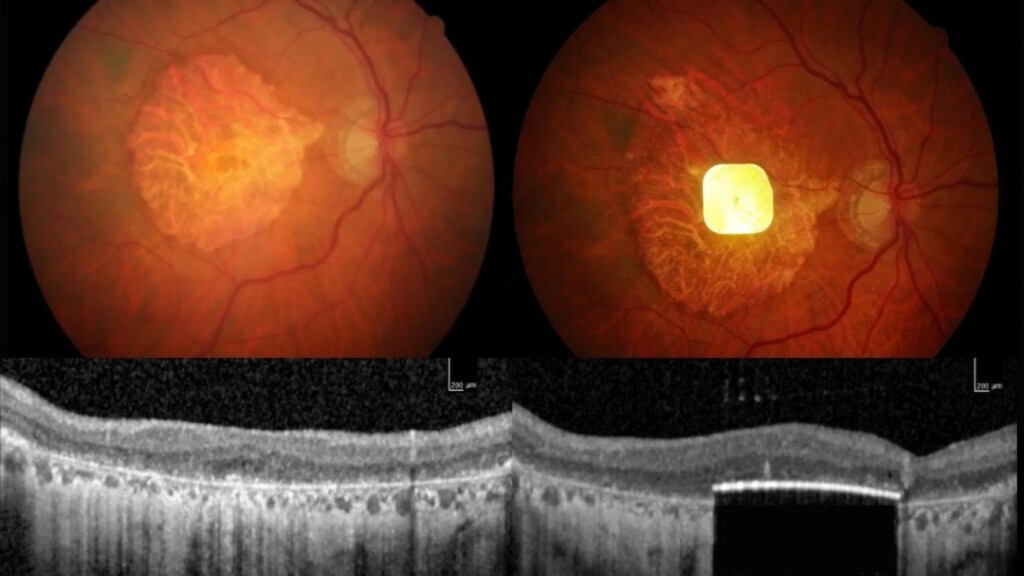 Scans of the implant in a patient’s eye – credit Science Corporation
Scans of the implant in a patient’s eye – credit Science CorporationThe procedure in install the implant involves a vitrectomy, where the eye’s vitreous jelly is removed from between the lens and the retina, and the surgeon inserts the ultra-thin microchip, which is shaped like a SIM card and just 2mm x 2mm.
The PRIMA System device used in this operation is being developed by Science Corporation, which develops brain-computer interfaces and neural engineering. No significant decline in existing peripheral vison was observed in trial participants, and these findings pave the way for seeking approval to market this new device.
UCL spoke with one of the patients who received the implant for the college’s news outlet.
“I wanted to take part in research to help future generations, and my optician suggested I get in touch with Moorfields,” began Sheila Irvine, one of Moorfields’ patients on the trial. “Before receiving the implant, it was like having two black discs in my eyes, with the outside distorted.
“I was an avid bookworm, and I wanted that back. I was nervous, excited, all those things. There was no pain during the operation, but you’re still aware of what’s happening. It’s a new way of looking through your eyes, and it was dead exciting when I began seeing a letter. It’s not simple, learning to read again, but the more hours I put in, the more I pick up.”
“The team at Moorfields has given me challenges, like ‘Look at your prescription,’ which is always tiny. I like stretching myself, trying to look at the little writing on tins, doing crosswords.”
The global trial was led by Dr. Frank Holz of the University of Bonn, with participants from the UK, France, Italy, and the Netherlands.
Mr. Muqit that it left him feeling that a door was opened for medical devices in this area, because there is no treatment currently licensed for dry AMD.“I think it’s something that, in future, could be used to treat multiple eye conditions.” A Combination Implant and Augmented Reality Glasses Restores Reading Vision to Blind Eyes


 The lion that escaped from a circus near Rome posed no threat to the public, his handler insisted Sunday, as campaigners called for Italy to ban wild animals in entertainment.
The lion that escaped from a circus near Rome posed no threat to the public, his handler insisted Sunday, as campaigners called for Italy to ban wild animals in entertainment.