 Shutterstock
Timothy Weber, Australian National University and Andrew Blakers, Australian National University
Shutterstock
Timothy Weber, Australian National University and Andrew Blakers, Australian National UniversityThe world is rapidly moving towards a renewable energy future. To support the transition, we must prepare back-up energy supplies for times when solar panels and wind turbines are not producing enough electricity.
One solution is to build more pumped hydro energy storage. But where should this expansion happen?
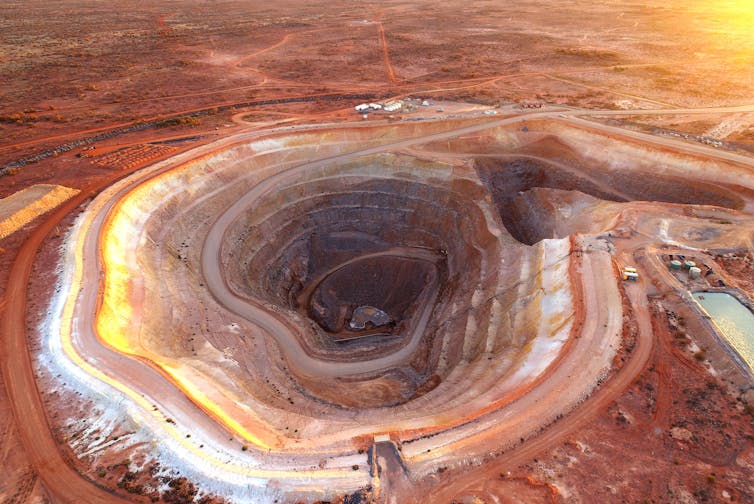
Our new research identified more than 900 suitable locations around the world: at former and existing mining sites. Some 37 sites are in Australia.
Huge open-cut mining pits would be turned into reservoirs to hold water for renewable energy storage. It would give the sites a new lease on life and help shore up the world’s low-emissions future.
The benefits of pumped hydro storage
Pumped hydro energy storage has been demonstrated at scale for more than a century. Over the past few years, we have been identifying the best sites for “closed-loop” pumped hydro systems around the world.
Unlike conventional hydropower systems operating on rivers, closed-loop systems are located away from rivers. They require only two reservoirs, one higher than the other, between which water flows down a tunnel and through a turbine, producing electricity.
The water can be released – and power produced – to cover gaps in electricity supply when output from solar and wind is low (for example on cloudy or windless days). And when wind and solar are producing more electricity than is needed – such as on sunny or windy days – this cheap surplus power is used to pump the water back up the hill to the top reservoir, ready to be released again.
Off-river sites have very small environmental footprints and require very little water to operate. Pumped hydro energy storage is also generally cheaper than battery storage at large scales.
Batteries are the preferred method for energy storage over seconds to hours, while pumped hydro is preferred for overnight and longer storage.
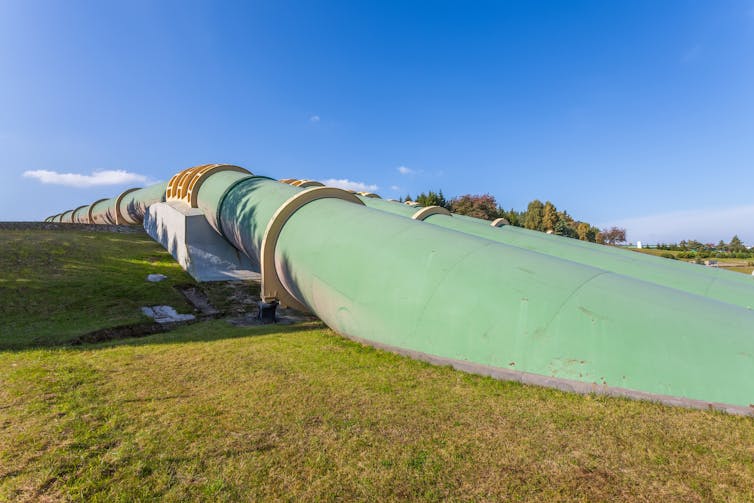 Pumped-hydro storage technology has been demonstrated at scale for over a century. Shutterstock
Pumped-hydro storage technology has been demonstrated at scale for over a century. ShutterstockWhy mining sites?
There are big benefits to converting mining areas into pumped hydro plants.
For a start, the hole has already been dug, reducing construction costs. What’s more, mining sites are typically already serviced by roads and transmission infrastructure. The site usually has access to a water source for which the mine operators may have pumping rights. And the development takes place on land that is already cleared of vegetation, avoiding the need to disturb new areas.
Finally, community support may have already been obtained for the mining operations, which could easily be rolled over into a pumped hydro site.
In Australia, one pumped hydro energy storage project is already being built at a former gold mine site at Kidston in Far North Queensland.
The feasibility of two others is being assessed at Mount Rawdon near Bundaberg in Queensland, and at Muswellbrook in New South Wales. Both would repurpose old mining pits.
What we found
Our previous research identified suitable locations in undeveloped areas (excluding protected land) and using existing reservoirs. Now, we have turned our attention to mine sites.
Our study used a computer algorithm to search the Earth’s surface for suitable sites. It looked for mining pits, pit lakes and tailings ponds in mining sites which were located near suitable land for a new upper reservoir. The idea is that the reservoir and mining site are “paired” and water pumped between them.
Globally, we identified 904 suitable mining sites across 77 countries.
Some 37 suitable sites are located in Australia. They include the Mount Rawdon and Muswellbrook mining pits already under investigation.
There are a number of potential options in Western Australia: in the iron-ore region of the Pilbara, south of Perth and around Kalgoorlie.
Options in Queensland and New South Wales are mostly located down the east coast, including the Coppabella Mine and the coal mining pits near the old Liddell Power Station. Possible sites also exist inland at Mount Isa in Queensland and at the Cadia Hill gold mine near Orange in NSW.
Potential sites in South Australia include the old Leigh Creek coal mine in the Flinders Ranges and the operating Prominent Hill mine northwest of Adelaide. Tasmania and Victoria also offer possible locations, although many other non-mining options exist in these states for pumped hydro storage.
We are not suggesting that operating mines be closed – rather, that pumped hydro storage be considered as part of site rehabilitation at the end of the mine’s life.
If old mining sites are to be converted into pumped hydro, several challenges must be addressed. For example, mine pits may contain contaminants that, if filled with water, could seep into groundwater. However, this could be overcome by lining reservoirs.
Looking ahead
Australia has set a readily achievable goal of reaching 82% renewable electricity by 2030.
The Australian Energy Market Operator suggests by 2050, this nation needs about 640 gigawatt-hours of dispatchable or “on demand” storage to support solar and wind capacity. We currently have about 17 gigawatt-hours of electricity storage, with more committed by Snowy 2.0 and other projects.
The 37 possible pumped hydro sites we’ve identified could deliver 540 gigawatt-hours of storage potential. Combined with other non-mining sites we’ve identified previously, the options are far more numerous than our needs.
This means we can afford to be picky, and develop only the very best sites. So what are we waiting for?![]()
Timothy Weber, Research Officer for School of Engineering, Australian National University and Andrew Blakers, Professor of Engineering, Australian National University
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.


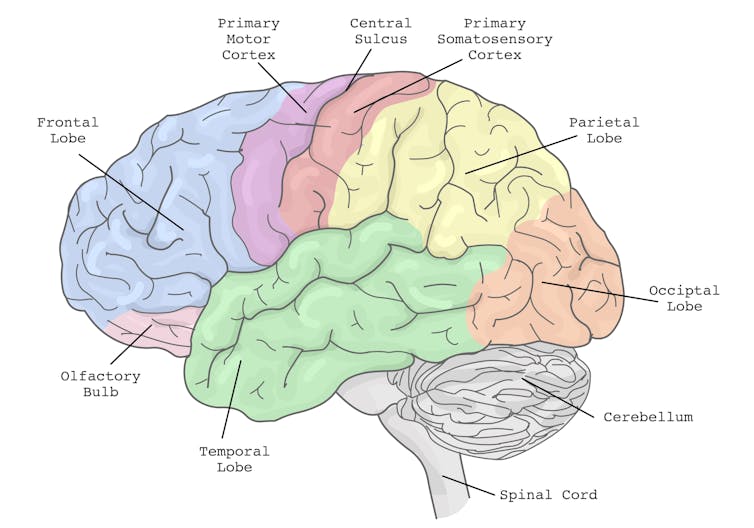 The brain’s action planning centres are in the frontal cortex (blue), with reciprocal connections to parietal cortex (yellow) and the cerebellum (grey), among others.
The brain’s action planning centres are in the frontal cortex (blue), with reciprocal connections to parietal cortex (yellow) and the cerebellum (grey), among others.  Having a conversation while driving slows your reaction time.
Having a conversation while driving slows your reaction time.  Our ability to multi-task reduces with age.
Our ability to multi-task reduces with age.