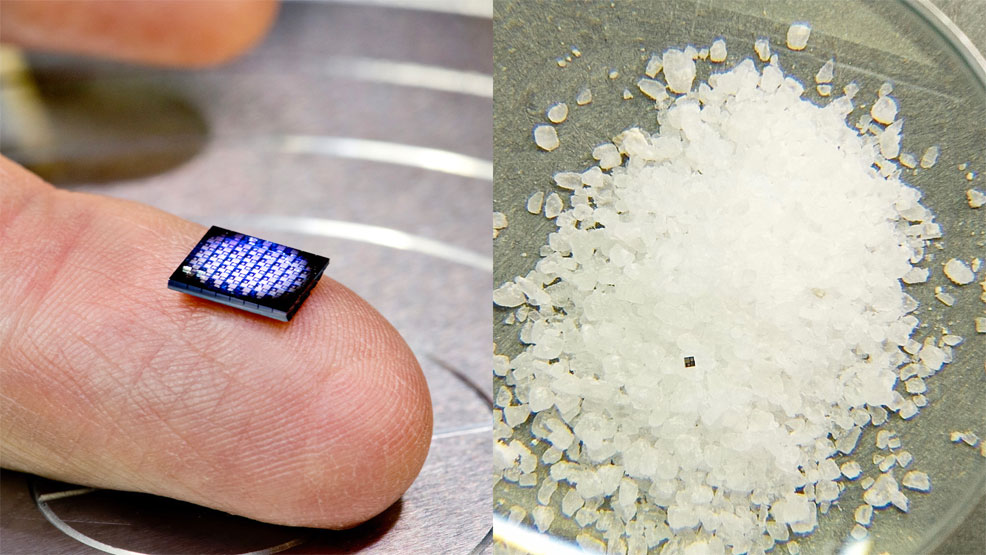
Credit: IBM Research
Most people are familiar with Moore's Law, but few have heard of Bell's Law – a related phenomenon coined by U.S. engineer Gordon Bell. This describes how a new class of computing devices tends to emerge about every decade or so, each 100 times smaller than the last. The shrinking volume of machines becomes obvious when you look back at the history of technology.
The 1960s, for example, were characterised by large mainframes that often filled entire rooms. The 1970s saw the adoption of "minicomputers" that were cheaper and smaller. Personal computing emerged in the early 1980s and laptops became popular in the 1990s. This was followed by mobile phones from the 2000s onwards, which themselves became ever thinner and more compact with each passing year, along with tablets and e-readers. More recently there has been rapid growth in wireless sensor networks that is giving birth to the Internet of Things (IoT).
The new computer announced by IBM is just 1mm x 1mm across, making it the smallest machine of its kind to ever be developed. It will feature as many as a million transistors, a solar cell and communications module. The company predicts these devices will be in widespread use within five years, embedded in all manner of everyday objects. So-called "cryptographic anchors" and blockchain technology...
