
RTSea: There you are, smartphone in hand, ready to engage in supersonic aerial combat. Or for more exercise, you stand in front of your television, clenching your game controller tightly, ready to play world-class tennis - game, set, match. Many of today's video games are aided by the use of accelerometers - electronic sensors that can recognize motion in a multitude of directions. Accelerometers have worked their way from aerospace and high-tech machinery applications to today's consumer electronics. And now they are adding another dimension to the study of sharks. At the Mote Marine Laboratory in Sarasota, Florida, Dr. Nick Whitney, head of Mote's Behavioral Ecology and Physiology Program, has been utilizing accelerometers in shark tags to advance the study of shark movements. "These accelerometer tags use the same technology found in iPhone[s] and Wii. It can actually tell us what an animal is physically doing, what their body movements are and what their body posture is," said Whitney. Correlating the data on shark movements with laboratory studies on oxygen consumption, Whitney is better able to make estimations of shark behavior, such as during mating or, in particular, during catch-and-release situations. Whether when promoting catch-and-release to sportfishermen or when catching sharks for scientific tagging and then releasing the shark, the extant to which a shark may be traumatized during the catch and how quickly it recovers is of great importance. a while to recover?" Whitney questioned, "Do they swim off strongly, doing great? Or does it take them
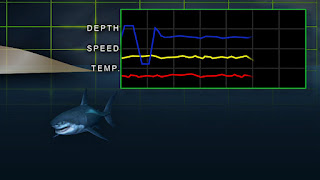 There are a wide range of telemetry tags used in shark research. Some are designed for regional behavior, monitoring a shark's depth, speed, and even internal body temperature. With a limited transmitting range, these tags are ideal for monitoring sharks within a shorter range of less than a mile. Dr. Peter Klimley at UC Davis as become one of the acknowledged masters of the art of regional telemetry tags and I have seen them used extensively with the white sharks at Isla Guadalupe, Baja. However, many sharks species are long-distance travelers and this is where "spot" or satellite tags are preferable. These more sophisticated tags record data for much longer periods of time, periodically downloading their data to satellite networks that surround the planet. Dr. Barbara Block, director of theTOPP Program (Tagging of Pelagic Predators), and Dr. Michael Domeier seen in National Geographic'sExpedition: Great White series, often make use of these types of tags, as do many other researchers for a variety of migratory shark species. With accelerometer tags, scientists like Dr. Whitney can get a glimpse of more than where a shark is, but how it's "feeling" as body movements can be correlated to its respiratory functions and overall metabolism at a given moment. Whitney will be soon starting a research study on blacktip sharks utilizing the accelerometer tags. I can't wait for the video game version to come out for my iPhone. Source: RTSea
There are a wide range of telemetry tags used in shark research. Some are designed for regional behavior, monitoring a shark's depth, speed, and even internal body temperature. With a limited transmitting range, these tags are ideal for monitoring sharks within a shorter range of less than a mile. Dr. Peter Klimley at UC Davis as become one of the acknowledged masters of the art of regional telemetry tags and I have seen them used extensively with the white sharks at Isla Guadalupe, Baja. However, many sharks species are long-distance travelers and this is where "spot" or satellite tags are preferable. These more sophisticated tags record data for much longer periods of time, periodically downloading their data to satellite networks that surround the planet. Dr. Barbara Block, director of theTOPP Program (Tagging of Pelagic Predators), and Dr. Michael Domeier seen in National Geographic'sExpedition: Great White series, often make use of these types of tags, as do many other researchers for a variety of migratory shark species. With accelerometer tags, scientists like Dr. Whitney can get a glimpse of more than where a shark is, but how it's "feeling" as body movements can be correlated to its respiratory functions and overall metabolism at a given moment. Whitney will be soon starting a research study on blacktip sharks utilizing the accelerometer tags. I can't wait for the video game version to come out for my iPhone. Source: RTSea