
Indian study finds 1st evidence on how nanoplastics from single-use PET bottles harm body

Scorpion Venom May Provide the Next Breast Cancer Breakthrough
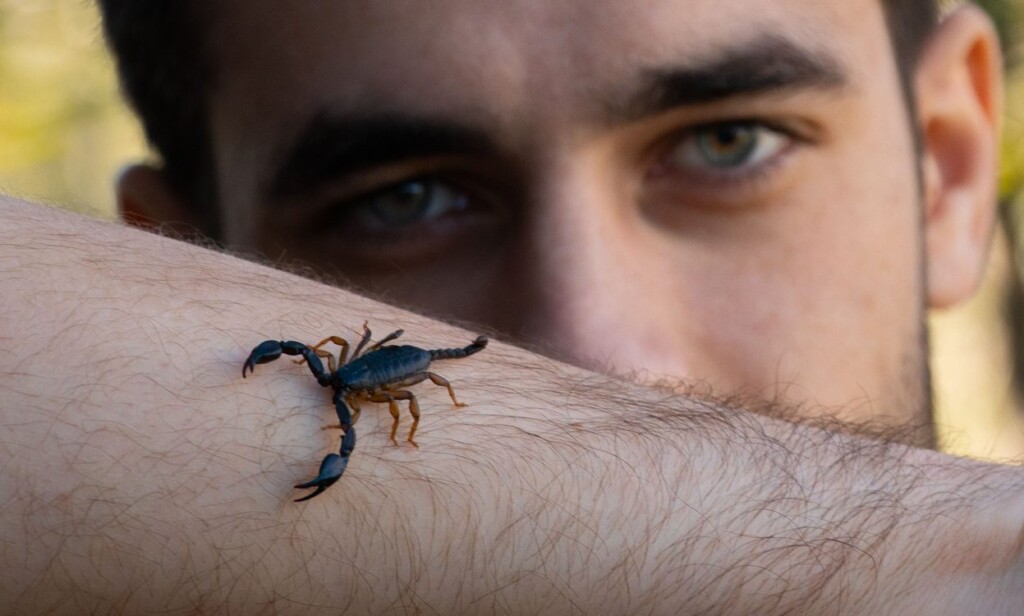 – credit Marino Linic
– credit Marino LinicScientists in Brazil are currently testing to see if the venom of an Amazonian scorpion could be used to poison breast cancer tumors.
Researchers at the University of São Paulo’s Preto School of Pharmaceutical Sciences (FCFRP-USP) have long worked to clone and express proteins from rattlesnake and scorpion venom with hopes of transforming these powerful compounds into medicines.
Recently, their work identified that venom of the scorpion Brotheas amazonicus appears to attack breast cancer cells in a way similar to a widely used chemotherapy medication.
These early findings were generated through a collaboration with scientists from the National Institute for Amazonian Research (INPA) and the Amazonas State University (UEA).
“Through bioprospecting, we were able to identify a molecule in the species of this Amazonian scorpion that is similar to that found in the venoms of other scorpions and that acts against breast cancer cells,” said Eliane Candiani Arantes, a professor at FCFRP-USP and the coordinator of the project.
Arantes and her team identified two neurotoxins in scorpion venom with immunosuppressive effects. Working with collaborators at INPA and UEA, they found a peptide named BamazScplp1 in the venom of Brotheas amazonicus that appears to have anti-tumor potential.
Laboratory tests showed that the peptide’s impact on breast cancer cells was comparable to paclitaxel, a commonly prescribed chemotherapy treatment. It primarily triggers necrosis, a form of cell death previously associated with molecules from other scorpion species.
Arantes and her team have isolated other components of venoms from scorpions and from snakes that have been used to help develop other clinical applications, including an internal wound sealant that mimics the body’s natural clotting and scaffolding processes. It’s undergoing trials for use in nerve repair, bone healing, and restoring movement following spinal cord injury.Next time you see a scorpion, and think it a nasty creepy crawly that will send you to the hospital, show a bit of grace; they might help save a woman’s life some day. Scorpion Venom May Provide the Next Breast Cancer Breakthrough
Indian scientists find genetic clues to tackle oral cancer among women

Australia leads first human trial of one-time gene editing therapy to halve bad cholesterol

ICRISAT develops portable technology for testing crops' nutrition level

Parkinson's disease causes progressive changes in brain's blood vessels: Study

Indian researchers develop smart portable device to detect toxic pesticides in water, food

Nanotechnology breakthrough may boost treatment for aggressive breast cancer: Study

Japanese researchers successfully regenerate bone using stem cells

Recyclers Switch from Smelting to Solvents, Recovering Precious Metals from E-waste with Fewer Emissions

Unique Antibody from Camels and Alpacas Could Be Used to Treat Alzheimer’s
 – credit, Sung Jin Cho on Unsplash
– credit, Sung Jin Cho on UnsplashNew online tool to transform how high blood pressure is treated
 IANS Photo
IANS PhotoNagaland University researchers find plant compound to treat diabetic wound, foot ulcers

Study shows eye scans may provide clues to ageing, heart disease risk
 (Photo: AI generated image/IANS)
(Photo: AI generated image/IANS)Rapid BP fluctuations may signal risk of brain degeneration in elderly

A Combination Implant and Augmented Reality Glasses Restores Reading Vision to Blind Eyes
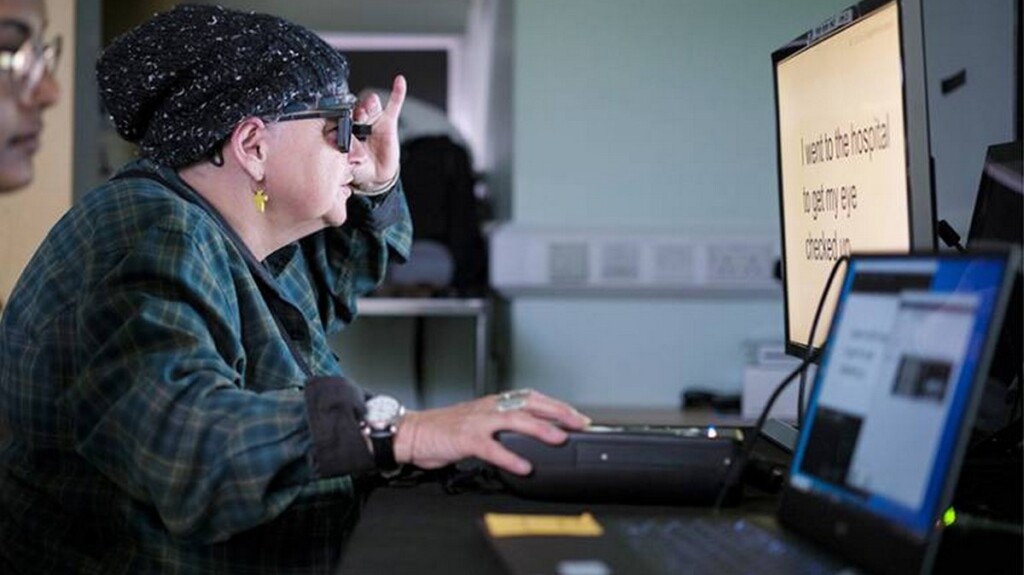 Study participant Sheila Irvine training with the device – credit Moorfields Eye Hospital
Study participant Sheila Irvine training with the device – credit Moorfields Eye Hospital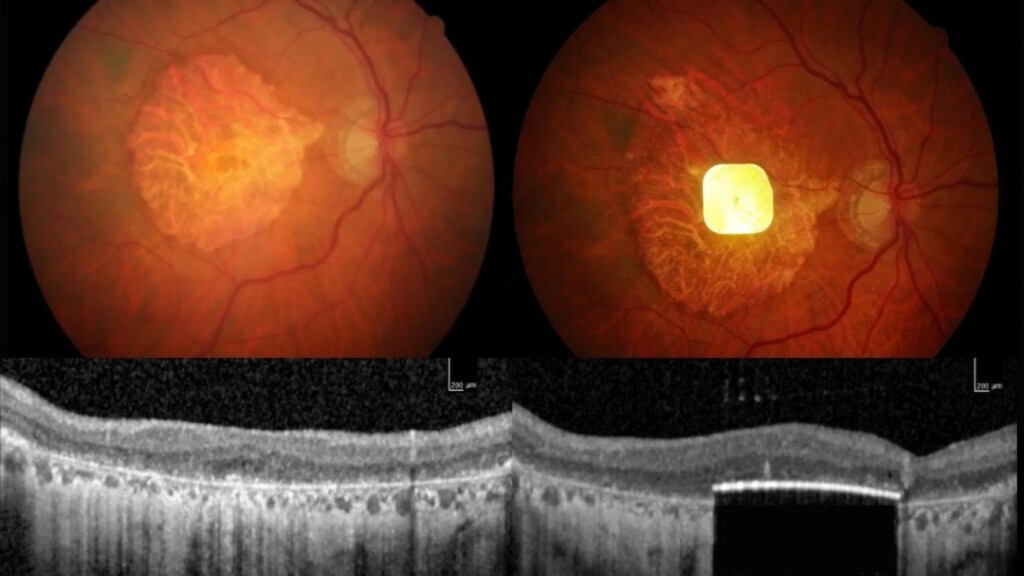 Scans of the implant in a patient’s eye – credit Science Corporation
Scans of the implant in a patient’s eye – credit Science CorporationFirst Antidote for Carbon Monoxide Poisoning 'Cleans' Blood in Minutes

Poor sleep may make your brain age faster – new study
Abigail Dove, Karolinska Institutet
We spend nearly a third of our lives asleep, yet sleep is anything but wasted time. Far from being passive downtime, it is an active and essential process that helps restore the body and protect the brain. When sleep is disrupted, the brain feels the consequences – sometimes in subtle ways that accumulate over years.
In a new study, my colleagues and I examined sleep behaviour and detailed brain MRI scan data in more than 27,000 UK adults between the ages of 40 and 70. We found that people with poor sleep had brains that appeared significantly older than expected based on their actual age.
What does it mean for the brain to “look older”? While we all grow chronologically older at the same pace, some people’s biological clocks can tick faster or slower than others. New advances in brain imaging and artificial intelligence allow researchers to estimate a person’s brain age based on patterns in brain MRI scans, such as loss of brain tissue, thinning of the cortex and damage to blood vessels.
In our study, brain age was estimated using over 1,000 different imaging markers from MRI scans. We first trained a machine learning model on the scans of the healthiest participants – people with no major diseases, whose brains should closely match their chronological age. Once the model “learned” what normal ageing looks like, we applied it to the full study population.
Having a brain age higher than your actual age can be a signal of departure from healthy ageing. Previous research has linked an older-appearing brain to faster cognitive decline, greater dementia risk and even higher risk of early death.
Sleep is complex, and no single measure can tell the whole story of a person’s sleep health. Our study, therefore, focused on five aspects of sleep self-reported by the study participants: their chronotype (“morning” or “evening” person), how many hours they typically sleep (seven to eight hours is considered optimal), whether they experience insomnia, whether they snore and whether they feel excessively sleepy during the day.
These characteristics can interact in synergistic ways. For example, someone with frequent insomnia may also feel more daytime sleepiness, and having a late chronotype may lead to shorter sleep duration. By integrating all five characteristics into a “healthy sleep score”, we captured a fuller picture of overall sleep health.
People with four or five healthy traits had a “healthy” sleep profile, while those with two to three had an “intermediate” profile, and those with zero or one had a “poor” profile.
When we compared brain age across different sleep profiles, the differences were clear. The gap between brain age and chronological age widened by about six months for every one point decrease in healthy sleep score. On average, people with a poor sleep profile had brains that appeared nearly one year older than expected based on their chronological age, while those with a healthy sleep profile showed no such gap.
We also considered the five sleep characteristics individually: late chronotype and abnormal sleep duration stood out as the biggest contributors to faster brain ageing.
A year may not sound like much, but in terms of brain health, it matters. Even small accelerations in brain ageing can compound over time, potentially increasing the risk of cognitive impairment, dementia and other neurological conditions.
The good news is that sleep habits are modifiable. While not all sleep problems are easily fixed, simple strategies: keeping a regular sleep schedule; limiting caffeine, alcohol and screen use before bedtime; and creating a dark and quiet sleep environment can improve sleep health and may protect brain health.
One explanation may be inflammation. Increasing evidence suggests that sleep disturbances raise the level of inflammation in the body. In turn, inflammation can harm the brain in several ways: damaging blood vessels, triggering the buildup of toxic proteins and speeding up brain cell death.
We were able to investigate the role of inflammation thanks to blood samples collected from participants at the beginning of the study. These samples contain a wealth of information about different inflammatory biomarkers circulating in the body. When we factored this into our analysis, we found that inflammation levels accounted for about 10% of the connection between sleep and brain ageing.
Other processes may also play a role
Another explanation centres on the glymphatic system – the brain’s built-in waste clearance network, which is mainly active during sleep. When sleep is disrupted or insufficient, this system may not function properly, allowing harmful substances to build up in the brain.
Yet another possibility is that poor sleep increases the risk of other health conditions that are themselves damaging for brain health, including type 2 diabetes, obesity and cardiovascular disease.
Our study is one of the largest and most comprehensive of its kind, benefiting from a very large study population, a multidimensional measure of sleep health, and a detailed estimation of brain age through thousands of brain MRI features. Though previous research connected poor sleep to cognitive decline and dementia, our study further demonstrated that poor sleep is tied to a measurably older-looking brain, and inflammation might explain this link.
Brain ageing cannot be avoided, but our behaviour and lifestyle choices can shape how it unfolds. The implications of our research are clear: to keep the brain healthier for longer, it is important to make sleep a priority.![]()
Abigail Dove, Postdoctoral Researcher, Neuroepidemiology, Karolinska Institutet
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.
The Subtle Power of Unhearable Sound: Mood and Cognition-Altering Agents

Indian researchers develop diagnostic device to detect early-stage bone cancer

